Description #
Twin and higher older multiple gestations are associated with increased risks to the woman and the offspring. Although every effort may be made to diagnose multiples early in pregnancy this may not always happen. Every midwife must be prepared to deal with undiagnosed twins during labour. This module outlines strategies for early diagnosis, appropriate antenatal and intrapartum considerations including attending undiagnosed twins.
Learning Objectives #
- List four intrapartum complications associated with vaginal birth of twins
- Describe safeguard measures during the birth of twins to reduce these risks.
- Describe the management for assisting in the birth of

Women pregnant with twins and higher order multiples face additional risks for themselves and their offspring. It is ideal to diagnose multiple gestations early in pregnancy to enable access to appropriate care. Multiple gestations are considered high risk. For this reason it is strongly recommended that women carrying multiples give birth in hospital with a consultant physician with skills in twin birth in attendance and with immediate access to the OR.
While maternal and fetal safety is significantly improved when birth is planned in a hospital setting with physician backup, midwives may find themselves faced with undiagnosed twin or even triplet gestations during labour.
In women who have not had a routine first- or second-trimester ultrasound, 38% of twin pregnancies remain unrecognized until after 26 weeks of gestation, and 13% of twins are diagnosed at birth (Chasen & Chervenak, 2007a)
Definitions #
Twins are a form of multiple pregnancy. The woman conceives and delivers two infants from one pregnancy. The babies can be identical (same sex) or fraternal (the same or opposite sex).
Twin pregnancies are classified by the Zygosity and Chorionicity.
Zygosity – the number of ova that were fertilized at conception.
Dizygotic (fraternal) – occurs when two ova are fertilized (two eggs, two sperm). They are siblings who share a womb and birthdate but carry their own unique genetic coding.
Monozygotic (Identical) – occur when a single ova is fertilized (one egg, one sperm) that then later divides in two. They are identical, will be the same sex and carry the same genetic DNA.
Monozygotic twins are further classified by their chorionicity and amnionicity:
Chorionicity & Amnionicity – describes the number of chorions and amnions surrounding the twins. The number depends on when the division occurred in the monozygotic pregnancy. It will be “mono” for one or “di” for two chorions/ amnions.
- Diamniotic, Dichorionic placentation arise when division takes place before the morula stage (within 3 days after fertilization). All dizygotic twins are in this category. One third (1/3) of monozygotic twins are included in this classification.
- Diamniotic, monochorionic placentation follows division between days 4 and 8 post fertilization. These will always be monozygotic twins.
- Monamniotic, monochorionic placentation occurs with division between days 8 and 12 after fertilization. All are monozygotic and may be mirror image twins (one twin is left-handed and the other is right-handed, opposite hair whorl directions).
Conjoined twins occur if the monozygotic cell division takes place at or after day 13. The separation will not be complete.
Note: The above process described for conceiving mono and dizygotic twins also contributes to higher order multiple of triplets, quads, etc.. These higher order multiples can be a result of either or both of these processes combined.
Incidence #

Incidence
In Canada spontaneous twin pregnancy occurs in 1 of 90 pregnancies (1.1%). Monozygotic twins occur in 3-5 per 1000 births (0.3-0.5%) and this rate does not vary across populations.
The rate of dizygotic twin and higher order multiples has risen significantly with advances in assisted reproductive technologies and advancing maternal age and now represents 3% of births in North America. Between 1973 and 1999 the rate rose by 35% in Canada. In addition to assisted reproduction, dizygotic twinning is influenced by maternal age (older), race, heredity, and parity (higher). Dizygotic twins occur more frequently in multiparous women over 35, of African descent and with a maternal family history of dizygotic twins.
Diagnosis #
Ultrasound is the reliable method of diagnosis and is recommended for women with higher risk of multiple gestation.
Twins should be suspected in a woman with the following:
· Uterine size larger than estimated gestational age
· Hyperemesis graviderum
· Excessive fetal movement
· Elevated maternal serum markers
· Generalized increased discomforted
· Abdominal exam notes lumpy contour and the fetal outline is difficult to palpate.
Antenatal Care
Early identification is recommended in multiple gestations to enable appropriate referral and surveillance. Chorionicity and dating can be determined between 10-14 weeks and will be critical to triaging the woman to the appropriate provider and centre for managing the pregnancy and birth.
The SOGC recommend that women with twin pregnancies be seen by or in conjunction with an obstetrician throughout pregnancy and that they have serial ultrasound exams every 2-4 weeks in the second and third trimester.
Refer to the SOGC Guidelines for Twin Pregnancy for recommendations regarding care of twin pregnancies.
Complications:
Multiple gestation increases risks to women and her fetuses / newborn.
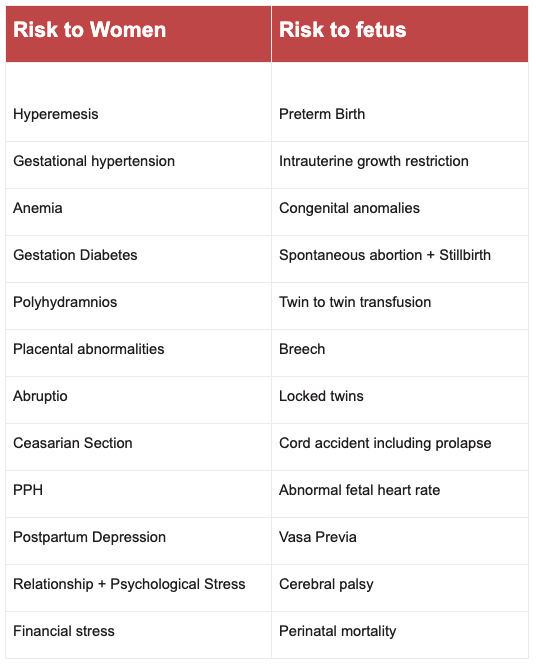
- Monochorionic twins have a 25% mortality rate related to their shared vascular system.
- Dichorionic twins have a 12% risk of mortality but do not share a vascular system
Birth of Twins
The SOGC recommend that women be informed of their options during the antenatal period.
Birth should be planned to occur in a hospital (CMBC, SOGC). Professionals trained in assisting with twin birth and neonatal resuscitation should be available. Bedside ultrasound, O.R. and anaesthesia is required. Someone with the skills to oversee a vaginal birth or conduct a C/S should be in attendance from the onset of labour. A primary care provider (family doctor or midwife) may be supervised in hands on care by the consultant physician.
The SOGC (2011) recommend the following for twin birth.

Vaginal birth is recommended unless there are contraindications to supporting this approach including consideration of the lie and presentation of both twins.
- Monochorionic monoamniotic twins are at very high risk of cord entanglement and thus often are delivered as early at 32 weeks by C/S.
- Non cephalic first twin should be reviewed in the same light as a singleton breech with the added very low risk of “locked” twins . Refer to the BREECH module for delivery of the breech.
Vaginal birth is supported if twin A is vertex and twin B is breech, as long as usual criteria for breech delivery are met and twin B is between 1500 and 4000 g (MOREob 2012).
Often twin B will start as vertex and flip to breech or transverse lie after twin A vacates the uterus. Breech extraction carries an increased risk of uterine rupture and fetal trauma. The breech with an extended head is at high risk of sustaining spinal cord injury during the birth process.
Managing vaginal birth of undiagnosed twins #

Considerations when Diagnosis of Twins occurs in labour
· Prepare the woman for possible C/S
· Start a large bore IV, and keep woman NPO, if the hospital will accept – draw blood for Crossmatch and CBC
· As many as three ambulances may be necessary if both infants and the mother are in need of resuscitation.
· Prepare to resuscitate TWO babies
· Active Management of the third stage (AMTSL) is highly recommended
o Do not give oxytocin until after the birth of the second twin
o Do NOT drain the cord of Twin A
o Do not do any cord traction after first twin
o After birth of second twin follow AMTSL protocol – both placentas are delivered at the same time
§ Administer Oxytocin 10 iu IM
§ Await signs of separation
§ With a contracted uterus and suprapubic counter-pressure do controlled cord traction holding BOTH cords to deliver placentas together
§ After completion of third stage assess fundus and massage as needed
o Consider adding Oxytocin 20IU to 1 litre of N/S to prevent uterine atony
· Mark the cords with single clamp on twin A’s and double clamp on Twin B’s – and send the placentas to pathology for histological examination.
· There has been no ongoing fetal assessment of both fetuses.
o Collect Cord blood samples and gases.
o Consider transfer to hospital for pediatric evaluation of twins, especially if discordant or any resuscitation was required.
Remember to follow up with the woman and family after the event. Frequent contact and increased support is essential to help them in the transition. They have been planning for one baby and now suddenly have two. They will require repeated explanations and opportunities to discuss the care they received.
Access community resources for additional breastfeeding support if required.
Parenting twins requires additional resources that this family may not have adequate access to, especially as they have not had time to prepare.
Postpartum Depression is increased in women with multiples. Ensure adequate screening and appropriate and timely referral in arranged.
Connect them with community resources including
http://www.multiplebirthscanada.org/
Document the care provided in detail.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Ailsworth, K., Anderson, J., Atwood, L.A., Bailey, R.E., & Canavan, T. (2006). ALSO: Advanced life support in obstetrics (4th ed.). Leawood, KS: American Academy of Family Practice Physicians.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2004b). Multiple gestation: Complicated twin, triplet, and high order multifetal pregnancy. Clinical management guidelines for OB-GYN (Practice Bulletin 56). Washington, DC: Author.
Barrett I, Bocking A. (2000) Management of twin pregnancies (part 2). Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada (SOGC) Consensus Statement. J SOGC.91:5–15.
Chasen, S.T., & Chervenak, F.A. (2004). Intrapartum management of twin gestations. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Chasen, S.T., & Chervenak, F.A. (2007a). Antepartum assessment of twin gestations. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Chasen, S.T., & Chervenak, F.A. (2007b). Delivery of twin gestations. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Cruikshank, D.P. (2007). Intrapartum management of twin gestations. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 109(5), 1167–1176.
Cunningham, F., Grant, N., Leveno, K., Gilstrap, L., Hauth, J., & Wenstrom, K. (2005). Williams’s obstetrics (22nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hofmeyr, G.J. (2007). Approach to breech presentation. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Howell, C., Grady, K., & Cox, C. (Eds.). (2007). Managing obstetric emergencies and trauma: The MOET course manual (2nd ed.) London: RCOG Press.
Jones, D.C. (2007). Triplet pregnancy: Mid and late pregnancy complications and management. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Queenan, J., Hobbins, J., & Spong, C. (Eds.). (2005). Protocols for high-risk pregnancies (4th ed). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
Roqué, H., & Lockwood, C.J. (2008). Monoamniotic twin pregnancy. In B.D. Rose (Ed.), UpToDate. Wellesley, MA: UpToDate.
Simpson, K.R., & Creehan, P.A. (2007). AWHONN’s perinatal nursing (3rd ed.). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Sinclair, C. (2004). A midwife’s handbook. St.
SOGC (2011) ALARM course syllabus 18th Ed, Authors: Ottawa.
- Material Resources Reading List
Select an item from the list below to download.
https://lms.can-health.org/content/663/text/SOGC_2000_Twin_pregnancy_part_1.pdf
https://lms.can-health.org/content/663/text/SOGC_2000_Twin_pregnancy_part_2.pdf
