Description #
This unit is designed to review basic respiratory anatomy and physiology with an emphasis on clinical relevance to physiotherapists and physiotherapy students. This unit will be administered online followed by a pre and post quiz. Accumulated knowledge from all of the units will be practiced and evaluated via case scenarios using the simulated patient.
Learning Objectives #
At the completion of this module the student will be able to:
- Identify anatomical structures.
- Identify anatomical landmarks.
- Understand the oxygen transport system.
Respiratory Anatomy (Unit) #
Key points #
Lung lobes and fissures
- The left lung is divided into superior and inferior lobes, and the right lung into superior, middle, and inferior lobes.
Pleura
- The lungs are covered with a double sheet of thin membrane which ensures that the lungs slide smoothly over the thoracic wall.
Bronchial Tree
- The bronchial tree originates at the trachea, splits into a right and left main bronchus. It then descends through the thorax in successively branching bronchus and terminating as millions of alveolar sacs.
Respiratory Membrane
- The alveoli provided a large surface area and a thin, permeable, and moist surface where the gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide can take place.
Muscles of Ventilation
- The main muscles of ventilation are the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles.
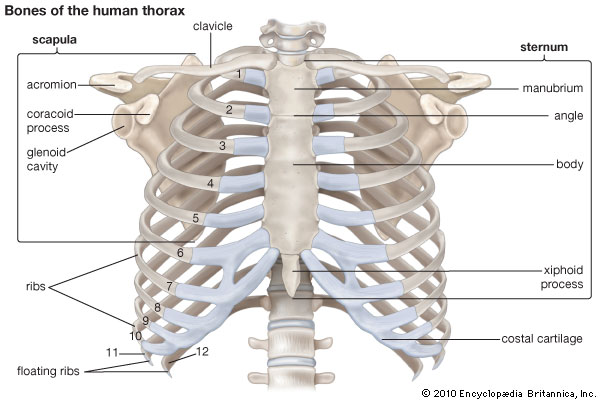
Sternum:
Manubrium – located at T3 – T4
Sternal angle – located at T4 – T5, level with the 2nd costal cartilage
Body of the sternum – located at T5 -T9
Xiphoid process – located at lower end of the sternum
Ribs:
1st – 6th ribs articulate onto the sternum via costal cartilages
7th- 10th ribs attach to costal cartilages
11th – 12th ribs are floating ribs
Mechanics:Pump handle – increases AP movement of the chest, occurs in the upper ribs.
Bucket handle – increases transverse diameter of the thorax and occurs in the lower ribs.
Scapula:
Inferior angle aligns with 7th intercostal space and the spinous process of T7.
Lungs #
The lungs are situated in the thoracic cavity, occupying most of the space either side of the mediastinum. Each of the cone-shaped lungs are suspended in a pleural cavity either side of the heart and are connected to the mediastinum by the hilum.

The following regions characterize each lung:
ApexThe apex is the most superior tip of each lung and protrudes above the clavicle.
HilumThe hilum is the triangular region on the medial surface of the lung through which the primary bronchi and neurovascular structures enter and leave.
BaseThe base of each lung is the inferior concave surface that rests on the diaphragm.
The lungs are supplied with deoxygenated blood via the pulmonary arteries and oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary veins to the heart.
The lung tissue itself is supplied with oxygenated blood via the bronchial arteries that are direct branches of the thoracic aorta.
The Heart #
Positioned in the centre of the chest behind the sternum. It is roughly equivalent in size to the individuals fist.
Apex:
Situated 9cm to the left of the 5th intercostal space.
Right border:Extends from 3rd – 6th costal cartilages approx. 10 – 15mm from sternum.
Left border:From 2nd costal cartilage 9mm from sternum to 5th intercostals space 15mm from sternal border.

Respiratory Tract #
Upper Respiratory Tract #
The upper respiratory tract refers to the nasal cavity, pharynx and their associated structures

Lower Respiratory Tract #
The lower respiratory tract refers to the larynx, bronchial tree, lungs and their associated structures.
Larynx and Epiglottis #
Epiglottis #
The epiglottis is a thin triangular flap of cartilage located at the entrance of the larynx. When food is swallowed, the epiglottis moves downwards and the larynx moves upwards, blocking off the entrance to the larynx.
Larynx #
The larynx or ‘voice box’ is a cartilaginous structure composed of several different cartilage elements; the thyroid, cricoid, epiglottis and two arytenoid cartilages. It has several very important functions, including protecting the airway and closing and sealing the lower respiratory tract, as well as being specialized to support voice production.
Bronchial Tree (Trachea to bronchioli) #
Trachea #
The trachea begins at the level of C6 below the cricoid cartilage of the larynx. It divides at the level of T4 (the Carina) into two principle bronchi. It is comprised of c-shaped tracheal cartilage rings anteriorly united by a fibroelastic membrane. Posteriorly, the gaps in the c-shaped cartilages are united by the trachealis muscle. Inside, the trachea is lined with cilia which beat upwards. This transports mucus and other inhaled particles, out of the lungs where they can be swallowed and neutralized in the stomach.
Carina #
The carina is a thick, incomplete cartilaginous ring that runs between the two primary bronchi at the bifurcation of the trachea.
Bronchi #
At the level of T4 the right and left main bronchi emerge as divisions of the trachea. They have a similar structure to the trachea with incomplete rings of cartilage anteriorly united by a fibroelastic membrane. They travel obliquely to enter each lung through the hilum, and begin dividing further into smaller branches.
It is important to note that the right bronchus is more vertical, shorter, and wider than the left. The left bronchus is more horizontal, longer, and thinner than the right.
There is one secondary bronchi for each lobe of the lungs: two on the left and three on the right.
Each of the tertiary bronchi serves a specific bronchopulmonary segment. There are ten tertiary bronchi in the right lung, and eight in the left lung. They do not have c-shaped cartilages, but instead have cartilaginous plates. They branch into bronchioles.
Bronchioli #
Also devoid of cartilage, the terminal bronchioles are largely composed of smooth muscle. These branch into respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles branch into several alveolar ducts, as well as having alveoli attached directly to them.
Alveoli #
The alveolar ducts are present on the distal end of the respiratory bronchioles. They branch into alveolar sacs, and are covered in alveoli. The terminal dilations of the alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, connect at least two alveoli.
There are 300 million alveoli in each lung, providing a large surface area for gas exchange. The alveoli are composed of a layer of type 1 ( in volved in Gas Diffusion) and Type 2 alveolar cells. Though fewer in number, Type 2 alveolar cells repair the alveolar wall after damage and secrete surfactant.
The internal surface of the alveoli is lined with alveolar fluid. It contains surfactant, a fluid rich in phospholipids and proteins and helps dissolve atmospheric Oxygen. The surfactant prevents the alveoli from sticking together with each breath by keeping the surface between the cells and air moist and thereby decreases the surface tension in the alveoli, preventing them from collapsing.
Physiology #
Key Points #
Pulmonary Ventilation
- The movement of air in and out of the lungs caused by pressure differences between the lung and the atmosphere resulting in changing lung volumes. During inhalation, air in the lungs is at a lower pressure than the atmosphere, so air flows into the lungs. The opposite is true for exhalation.
Gas Exchange
- Is governed by the difference in partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) on either side of the respiratory membrane (gases move from an area of high partial pressure to an area of low partial pressure).
Control Of Respiration
- Our respiratory rate and the depth at which we breath is controlled by the respiratory center, located in the brainstem (Medulla Oblangata and Pons). It ensures that our respiratory effort matches the metabolic demands of our body.
Gas Exchange #
Please watch this short video below with summarizes Gas Exchange.
External Respiration #
External respiration refers to the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in our alveoli and the blood in our pulmonary circulation. Oxygen moves from the air in the alveoli into the blood in the pulmonary circulation, whereas carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction. The rate at which these gases diffuse is dependent on their partial pressures.
Oxygen (O2) #
Typically, the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in the air within the alveoli is 105 mm Hg compared with 40 mm Hg in the pulmonary capillaries. As a result, oxygen will tend to move out of the air within the alveoli and into the capillaries.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) #
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) is 40 mm Hg in the air within the alveoli, and 45 mm Hg in blood of the pulmonary capillaries. This tends to make the carbon dioxide move from the blood into the air within the alveoli removing carbon dioxide from the body.
Internal Respiration #
Internal respiration refers to the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the cells of our body and the blood in our systemic capillaries. Oxygen moves from the systemic capillaries into tissues, whereas carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction. The rate at which these gases diffuse is dependent on their partial pressures.
Oxygen (O2) #
Normally, the partial pressure of oxygen in tissues is 40 mm Hg versus 100 mm Hg in capillaries, so oxygen will tend to move out of the capillaries and into the tissues.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) #
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 45 mm Hg in tissues, and 40 mm Hg in systemic capillaries, which tends to make carbon dioxide move from the tissues into the capillaries.
